The 4 Stages of Sleep
Types of Sleep Disorders
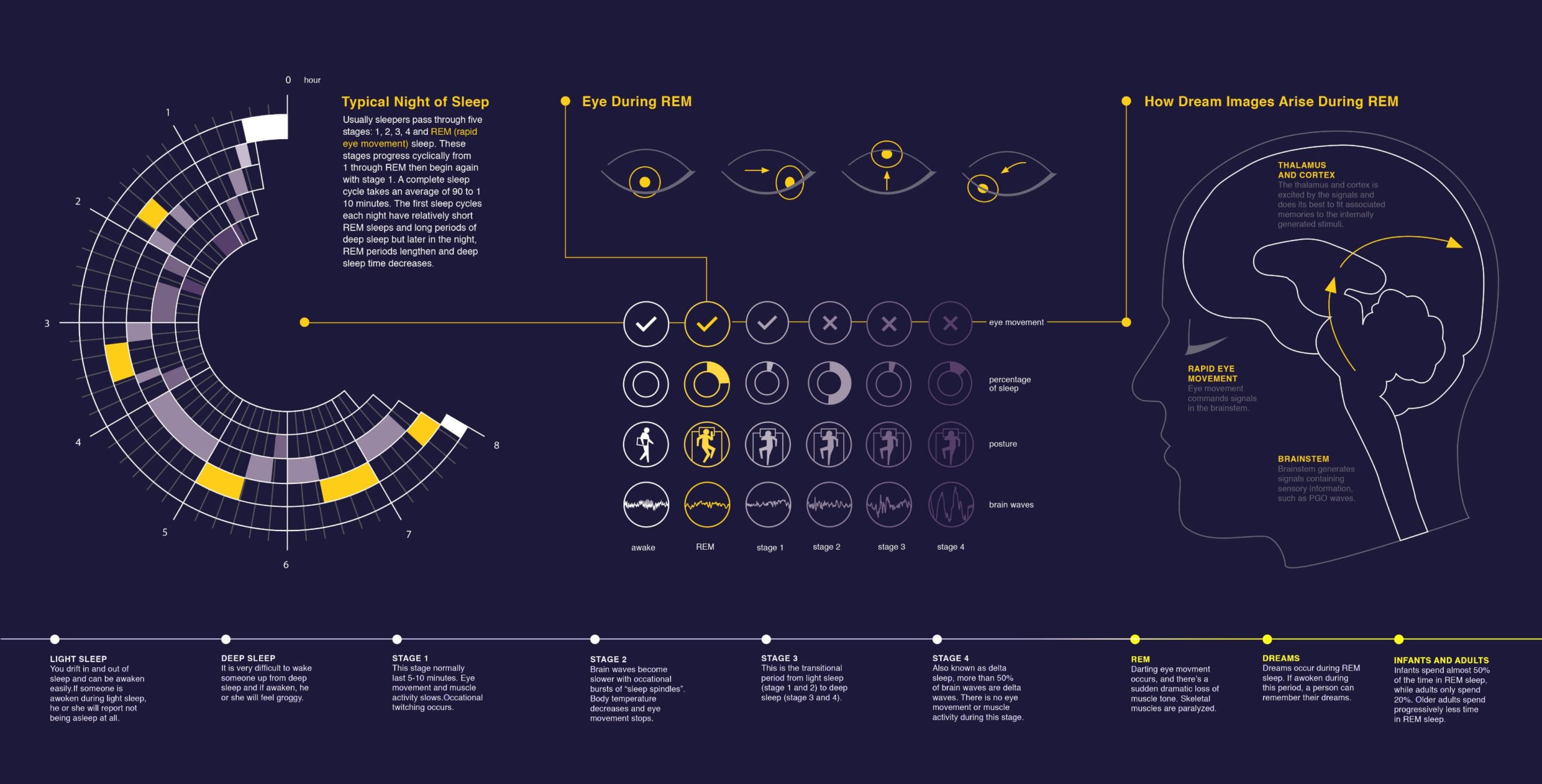
STAGE 1
STAGE 2
STAGE 3
This is the final stage of any standard sleep cycle. The first Rapid Eye Movement (REM) sleep lasts around 10 minutes and usually happens after having been asleep at least 90 minutes.
Usually, REM sleep happens 90 minutes after you fall asleep. The first period of REM typically lasts 10 minutes. Each of your later REM stages gets longer, and the final one may last up to an hour. Your heart rate and breathing quickens. You can have intense dreams during REM sleep, since your brain is more active.
Breathing becomes more rapid and irregular during REM sleep than during non-REM sleep, and the heart rate and blood pressure also increase to near waking levels. Core temperature is not well regulated during this time and tends towards the ambient temperature. Although the muscles become more relaxed during non-REM sleep, they become completely paralyzed and unresponsive during REM sleep.
Babies can spend up to 50% of their sleep in the REM stage, compared to only about 20% for adults.